Authors: Akshat Gupta, Laxman Singh Tomar, Ridhima Garg
Abstract
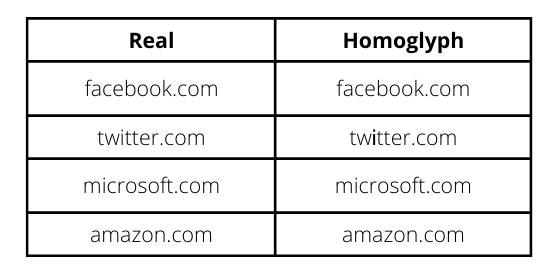
Cyber attacks deceive machines into believing something that does not exist in the first place. However, there are some to which even humans fall prey. One such famous attack that attackers have used over the years to exploit the vulnerability of vision is known to be a Homoglyph attack. It employs a primary yet effective mechanism to create illegitimate domains that are hard to differentiate from legit ones. Moreover, as the difference is pretty indistinguishable for a user to notice, they cannot stop themselves from clicking on these homoglyph domain names.
In our work, we created GlyphNet, an image dataset that contains 4M domains, both real and homoglyphs. Additionally, we introduce a baseline method for homoglyph attack detection system using an attention-based convolutional Neural Network. We show that our model can reach state-of-the-art accuracy in detecting homoglyph attacks with a 0.93 AUC on our dataset.
Introduction
In cyber security, attackers employ different attacks to infiltrate our systems and networks, with the objective varying from stealing crucial information to inflicting system damage. One such deceptive attack is the homoglyph attack, which involves an attacker trying to fool humans and computer systems by using characters and symbols that may appear visually similar to characters used in real domain and process names but are different.
Dataset
Proposed Dataset
We have proposed a dataset consisting of real and homoglyph domains. We obtained domains from the Domains Project, comprising 500M domains, restricting our work to 2M domains due to hardware restrictions.
Homoglyph Creation Algorithm
We created a novel algorithm for the generation of homoglyph domains to ensure that real homoglyphs are generated with randomness and closeness. To achieve this, we sample homoglyph noise characters using Gaussian sampling from the glyph pool.
Image Generation
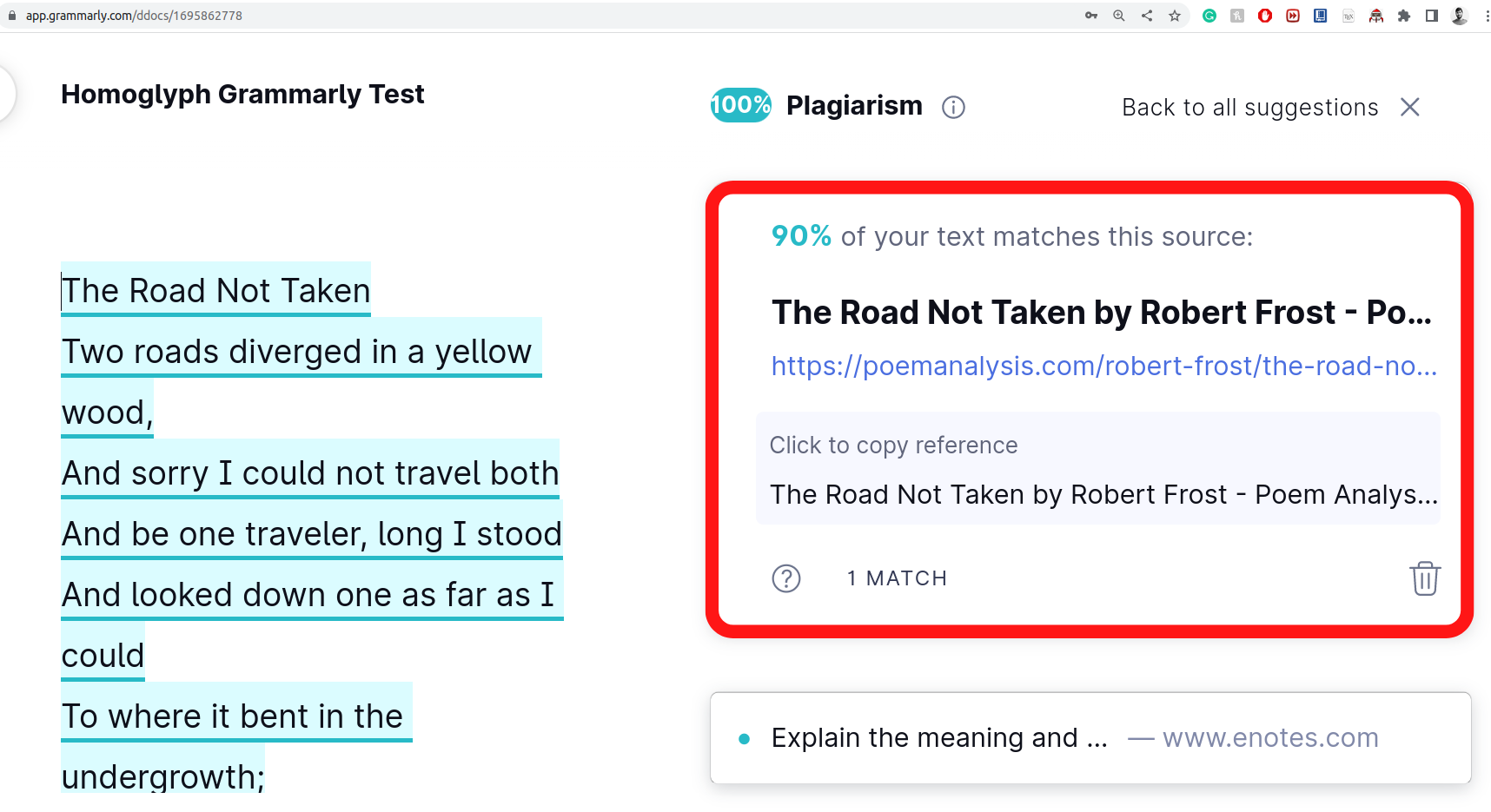
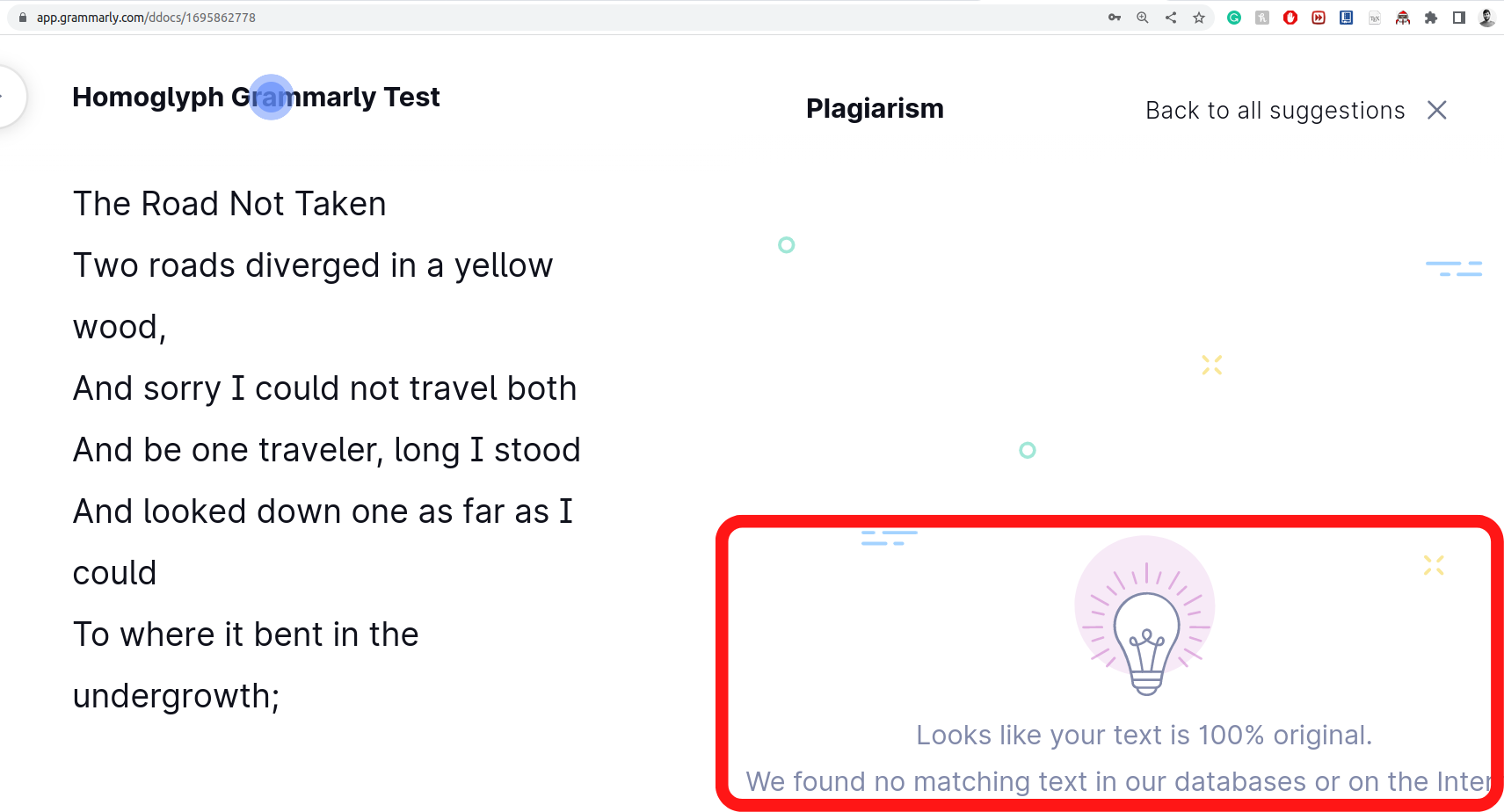
Homoglyph attacks exploit the weakness of human vision to differentiate real from homoglyph domain names. We rendered images from the real and homoglyph strings generated via our algorithm.
Methodology
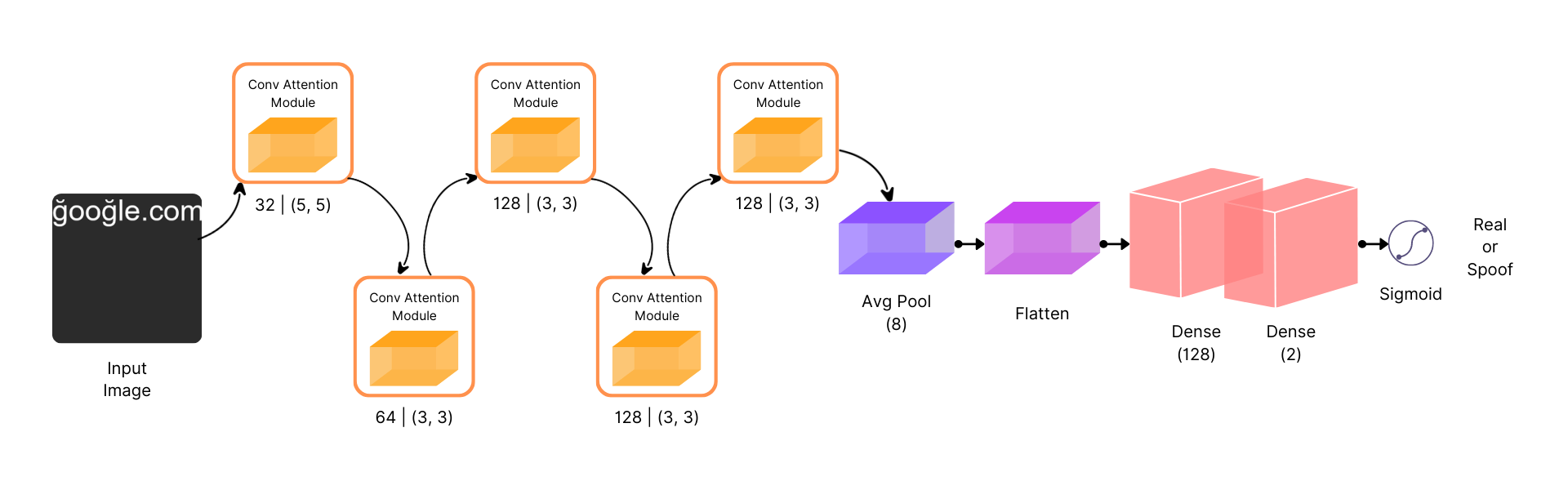
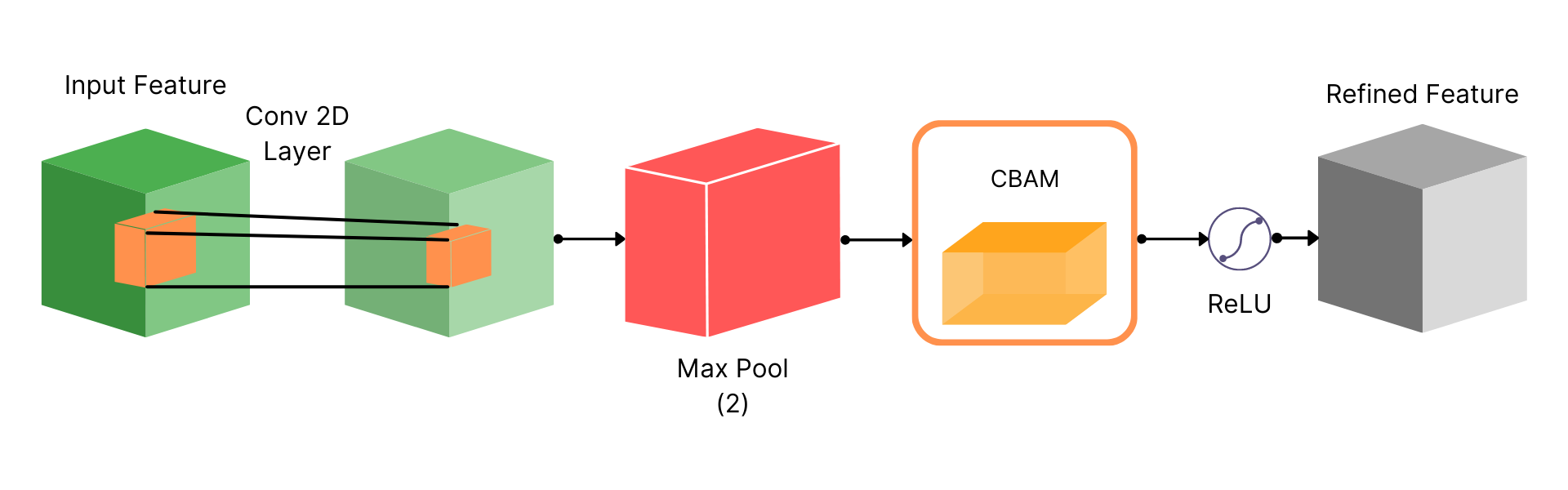
Experimentation
Dataset and Metrics
We split our dataset into train, validation, and test, with a ratio of 70:20:10, respectively. We use accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score as our evaluation metrics, along with the AUC score.
Experimental Settings
For training, we used binary cross-entropy as a Loss Function and RMSProp Optimizer. The network is trained for 30 epochs with early stopping, using a batch size of 256.
Results
We evaluated our model on two unpaired datasets for domain names, achieving an accuracy of 0.93 and an F1-score of 0.93, outperforming other models.
References
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; and Bengio, Y. 2014. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473.
- Boor, V.; Overmars, M. H.; and Van Der Stappen, A. F. 1999. The Gaussian sampling strategy for probabilistic roadmap planners. In Proceedings 1999 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 99CH36288C), volume 2, 1018–1023. IEEE.
- Cheng, L.; Liu, F.; and Yao, D. 2017. Enterprise data breach: causes, challenges, prevention, and future directions. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 7(5): e1211.
- Chollet, F.; et al. 2015. Keras. Damerau, F. J. 1964. A technique for computer detection and correction of spelling errors. Communications of the ACM, 7(3): 171–176.
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; and FeiFei, L. 2009. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 248–255. Ieee.
- Ginsberg, A.; and Yu, C. 2018. Rapid homoglyph prediction and detection. In 2018 1st International Conference on Data Intelligence and Security (ICDIS), 17–23. IEEE.
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; and Bengio, Y. 2014. Generative adversarial nets. Advances in neural information processing systems, 27.
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; and Sun, J. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 770–778.
- Helms, M. M.; Ettkin, L. P.; and Morris, D. J. 2000. The risk of information compromise and approaches to prevention. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 9(1): 5–15.
- Hoffer, E.; and Ailon, N. 2015. Deep metric learning using triplet network. In International workshop on similarity-based pattern recognition, 84–92. Springer.
- Hong, J. 2012. The state of phishing attacks. Communications of the ACM, 55(1): 74–81.
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; and Efros, A. A. 2017. Imageto-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 1125–1134.
Citation
@article{gupta2023glyphnet,
title={GlyphNet: Homoglyph domains dataset and detection using attention-based Convolutional Neural Networks},
author={Gupta, Akshat and Tomar, Laxman Singh and Garg, Ridhima},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.10392},
year={2023}
}